Income Statements: Variable Cost vs Absorption Cost
The over-absorbed fixed costs need to be subtracted from the cost of sales. Calculate gross profit by subtracting the cost of goods sold from sales. Costs are separated as variable and fixed (cost behavior) which is helpful for internal analysis. The following diagram explains the cost flow for product and period costs. If less than the budgeted units were manufactured, then we would have to add them to the cost of sales. Sales revenue was calculated by multiplying sold units (140,000) by the selling price ($10) to arrive at $1400,000.
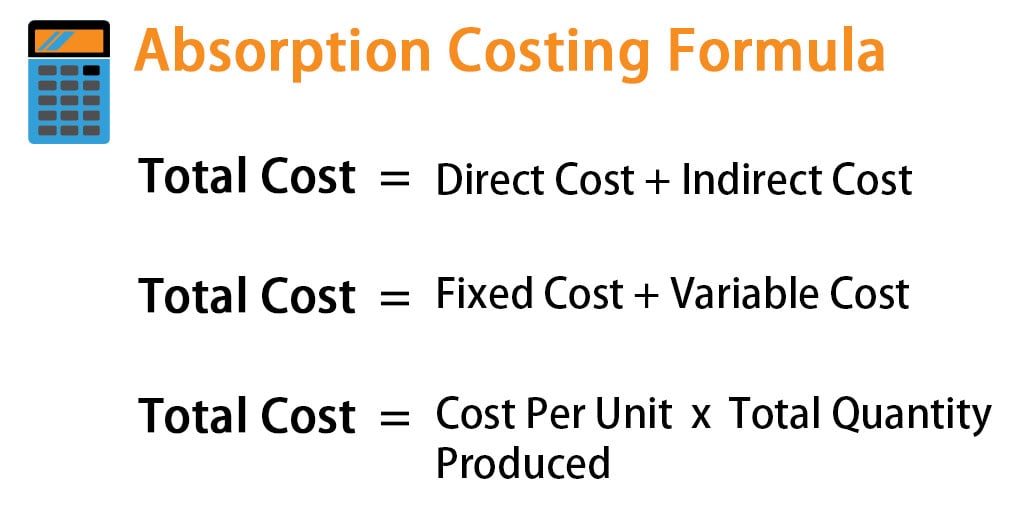
Absorption Rate
It helps company to calculate cost of goods sold and inventory at the end of accounting period. It is necessary to note that there would always be an imbalance in the balance sheet of absorption cost; the inventory is always higher than the expenses on an income statement. This is because an absorption cost includes manufacturing products, employees’ wages, raw materials, and every other production cost. Absorption costing is also often used for internal decision-making purposes, such as determining the selling price of a product or deciding whether to continue producing a particular product. Based on absorption costing methods, the additional unit appears to produce a loss of $0.50, and it appears that the correct decision is to not make the sale.
What is absorption costing under GAAP?
- Because absorption costing includes fixed overhead costs in the cost of its products, it is unfavorable compared with variable costing when management is making internal incremental pricing decisions.
- Cost of goods sold includes direct materials, direct labor, and variable and allocated fixed manufacturing overhead.
- It is a very common method used widely in the business especially in the manufacturing sector, and in this way the company is able to determine the cost of individual product and services.
- Once the cost pools have been determined, the company can calculate the amount of usage based on activity measures.
- Variable costing suggests a profit of $0.50, and the information appears to support a decision to make the sale.
Because fixed costs are spread across all units manufactured, the unit fixed cost will decrease as more items are produced. Therefore, as production increases, net income naturally rises, because the fixed-cost portion of the cost of goods sold will decrease. The components of absorption costing include both direct costs and indirect costs. Direct costs are those costs that can be directly traced to a specific product or service.
Over absorption of Fixed Cost
For example, recall in the example above that the company incurred fixed manufacturing overhead costs of $300,000. If a company produces 100,000 units (allocating $3 in FMOH to each unit) and only sells 10,000, a significant portion of manufacturing overhead costs would be hidden in inventory in the balance sheet. If the manufactured products are not all sold, the income statement would not show the full expenses incurred during the period. In addition, absorption costing takes into account all costs of production, such as fixed costs of operation, factory rent, and cost of utilities in the factory.
What’s the Difference Between Variable Costing and Absorption Costing?
These differences are due to the treatment offixed manufacturing costs. Under absorption costing, each unit inending inventory carries $0.60 of fixed overhead cost as part ofproduct cost. Therefore, ending inventory under absorption costingincludes $600 of fixed manufacturing overhead costs ($0.60 X 1,000units) and is valued at $600 more than under variable costing. The difference between the absorption and variable costing methods centers on the treatment of fixed manufacturing overhead costs.
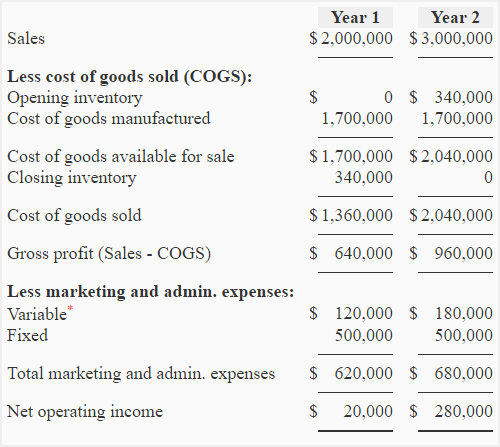
Selling, general, and administrative costs (SG&A) are classified as period expenses. Under full absorption costing, variable overhead and fixed overhead are included, meaning it allocates fixed overhead costs to each unit of a good produced in the period–whether the product was sold or not. The treatment of fixed disaster relief resource center for tax professionals overhead costs is different than variable costing, which does not include manufacturing overhead in the cost of each unit produced. Absorption costing allocates all manufacturing costs, including fixed overhead costs, to the units produced. This differs from variable costing, which only allocates variable costs.
Finally, remember that the difference between theabsorption costing and variable costing methods is solely in thetreatment of fixed manufacturing overhead costs and incomestatement presentation. Regarding selling andadministrative expenses, the only difference is their placement onthe income statement and the segregation of variable and fixedselling and administrative expenses. Variable selling andadministrative expenses are not part of product cost under eithermethod. Absorption costing is an inventory valuation method that allocates all manufacturing costs, including both variable costs and fixed overhead costs, to the units produced. This means that inventory is valued to include both direct costs of materials and labor as well as a portion of fixed manufacturing overhead costs. Absorption costing is a method in which cost of units produced is calculated as the sum of both the variable manufacturing costs incurred and the fixed manufacturing costs allocated to those units.
When doing an income statement, the first thing I always do is calculate the cost per unit. Under absorption costing, the cost per unit is direct materials, direct labor, variable overhead, and fixed overhead. In this case, the fixed overhead per unit is calculated by dividing total fixed overhead by the number of units produced (see absorption costing post for details).
Kristin is also the creator of Accounting In Focus, a website for students taking accounting courses. Since 2014, she has helped over one million students succeed in their accounting classes. The amount of under-absorption is added to the cost of items created and sold if the actual output level is less than the normal output level. Once you have viewed this piece of content, to ensure you can access the content most relevant to you, please confirm your territory.
As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy. It is required in preparing reports for financial statements and stock valuation purposes. Therefore, it is necessary to analyse and evaluate the pros and cons of the process and then decide whether it is suitable for the business.
Determining the appropriate costing system and the type of information to be provided to management goes beyond providing just accounting information. The costing system should provide the organization’s management with factual and true financial information regarding the organization’s operations and the performance of the organization. Unethical business managers can game the costing system by unfairly or unscrupulously influencing the outcome of the costing system’s reports. Use a different format for each (see above), however, all amounts will be the same on both statements with the exception of fixed manufacturing overhead.

